Metronidazole is a common drug found on the shelves of veterinary hospitals and pharmacies. This antibiotic is used to treat a number of different ailments and has become very important to veterinary patients, although its use in dogs and cats is considered extra-label in the United States. So, continue reading below to learn about the dosages, uses, and potential side effects of this drug for cats specifically.


What is Metronidazole?
Metronidazole, or Flagyl, is an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal drug often used to treat conditions that cause diarrhea. This drug is useful against common protozoan parasites including Giardia and anaerobic bacteria. In addition to infectious causes, it helps control inflammatory bowel disease and hepatic encephalopathy. Metronidazole has anti-inflammatory effects.
Dosage recommendations vary depending on the disease being treated. Care should be taken in administering the medication as prescribed by the provider.
It is also important to follow the storage information found on the medication packaging, as storage recommendations may differ between compounded products.
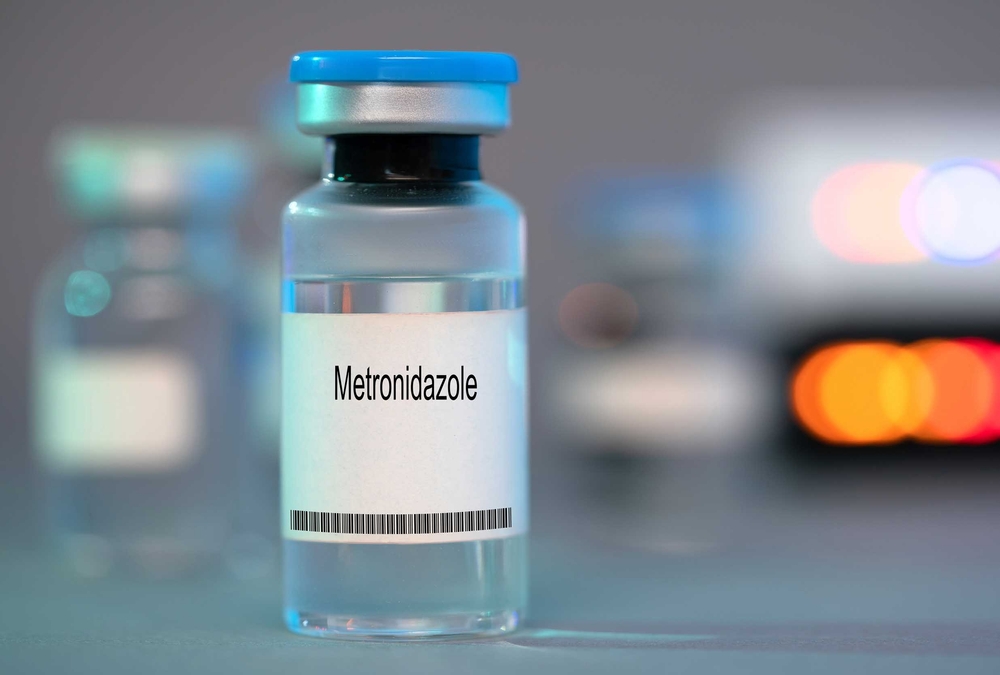
How is Metronidazole Given?
Metronidazole can be given orally as a liquid, capsule, or tablet. It is also available in an injection form for use within a hospital setting. Metronidazole is often bitter and the taste can be difficult to mask, making it difficult to administer, especially to cats. Compounded metronidazole benzoate is more easily tolerated by cats, as it is less bitter.
Metronidazole is generally given twice daily. Some conditions that require long-term Metronidazole treatment may be ameliorated with once-daily dosing. In case of accidental overdose, contact your veterinarian.
Potential Side Effects of Metronidazole
What Happens If You Miss a Dose?
If a dose of metronidazole is missed, you can give it when you remember, but then you must wait the recommended interval before giving the next dose. Do not double the dose.
Risk of Metronidazole Toxicity
Some animals may experience neurotoxicity from metronidazole. This is most likely to occur in animals at high doses of the drug, following an accidental overdose, or in those receiving Metronidazole for a long time. Signs of neurotoxicity include nystagmus, seizures, and head tilt, among other signs. If this is noticed in your pet while on metronidazole, stop and contact your prescribing veterinarian.

Precautions
This drug should be used with caution in animals with liver disease. Animals with liver concerns should receive a reduced dose. Patients with severe renal impairment may also require lower doses. Administration of metronidazole to pregnant animals should be avoided.
Drug interactions
Care should be taken if administering Metronidazole concurrently with the following drugs, and your veterinarian should be consulted:
- Barbiturates (Phenobarbital)
- Phenytoin
- Warfarin
- Cimetidine
- Terfenadine
- Vitamin K Antagonists
- Lithium
- Calcineurin inhibitors
- Cyclosporine


Frequently Asked Questions
Is Metronidazole Safe to Use in a Pregnant Cat?
No, it is not recommended to use Metronidazole in pregnant animals, as it can cause birth defects.
Should this medicine be given with food?
This medication should be taken with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal upset.
If Neurotoxicity Occurs, Are the Signs Permanent?
Signs of neurotoxicity may resolve when the drug is discontinued. This may take several days to weeks. Diazepam may help improve clinical signs more quickly. Neurotoxicity from Metronidazole is rarely fatal.

In summary
Metronidazole is a commonly used antibiotic/antiparasitic agent. The risk of neurotoxicity exists, but it is usually the result of prolonged dosing or the use of high doses. It is important to discuss any medications your pet is taking with your prescribing veterinarian before starting Metronidazole or any other medication. Close observation of your pet while on Metronidazole is recommended to ensure that improvements are noted in clinical signs and to monitor for adverse effects.
Featured Image Credit: Sonis Photography, Shutterstock



